Audio Frequency & Hearing
QUOTE:
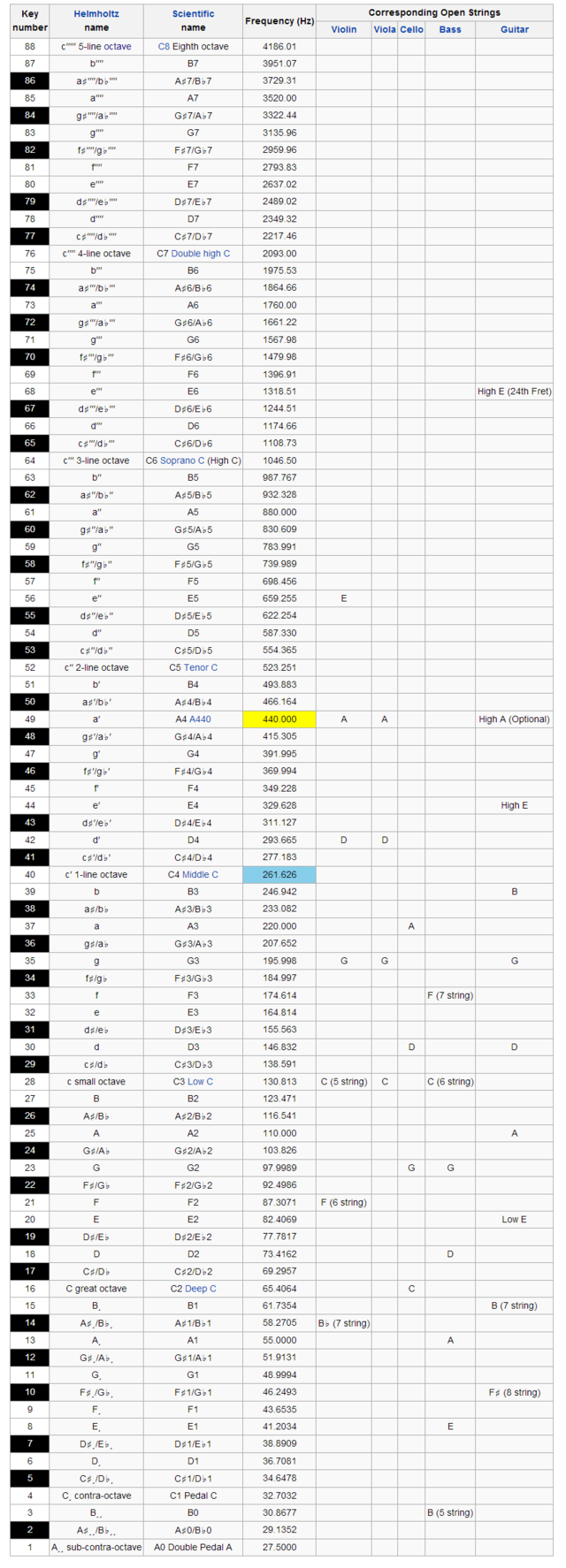
An audio frequency (abbreviation: AF) or audible frequency is characterized as a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human. It is the property of sound that most determines pitch and is measured in hertz (Hz).
The generally accepted standard range of audible frequencies is 20 to 20,000 Hz, although the range of frequencies individuals hear is greatly influenced by environmental factors. Frequencies below 20 Hz are generally felt rather than heard, assuming the amplitude of the vibration is great enough. Frequencies above 20,000 Hz can sometimes be sensed by young people. High frequencies are the first to be affected by hearing loss due to age and/or prolonged exposure to very loud noises.
END QUOTE:
I’ll add that in sound system design, 30hz to 18,000hz is considered the range of interest. A low B on a 5 string bass is 30.868hz so obviously a sound system must be able to reach down to at least 30hz. Unless you’re a new born baby or a small child, it’s typical to expect that you will have already lost some high frequency hearing by the time you reach adulthood.
Different animals hear in different frequency ranges.
An elephant can hear down to below 20hz but have less HF hearing that humans. This makes sense because elephants communicate over long distances using low frequencies. Dolphins, whales, porpoises and bats can hear above 100,000hz. Obviously each branch of the animal kingdom has a hearing mechanism optimized for their specific needs.